INFO4DISASTER PAGES
Wednesday, March 23, 2011
Wednesday, March 16, 2011
Monday, March 14, 2011
Tsunami Hazards
Things You Should Know:
- Although tsunamis in California are a rare, the entire California coastline is vulnerable to these events.
- A tsunami is a series of waves or surges most commonly caused by an earthquake beneath the sea floor.
- An unusual lowering of ocean water, exposing the sea floor, is a warning of a tsunami or other large wave. This “draw back” means the water will surge back strongly.
- Beaches, lagoons, bays, estuaries, tidal flats, and river mouths are the most dangerous places to be. It is rare for a tsunami to penetrate more than a mile inland.
- Tsunami waves are unlike normal coastal waves. Tsunamis are more like a river in flood or a sloping mountain of water and filled with debris.
- Tsunamis cannot be surfed. They have no face for a surfboard to dig into and are usually filled with debris.
- Large tsunamis may reach heights of twenty to fifty feet along the coast and even higher in a few locales.
- The first tsunami surge is not the highest and the largest surge may occur hours after the first wave.
- It is not possible to predict how many surges or how much time will elapse between waves for a particular tsunami.
Are You Ready?
Tsunamis
Tsunamis (pronounced soo-ná-mees), also known as seismic sea waves (mistakenly called “tidal waves”), are a series of enormous waves created by an underwater disturbance such as an earthquake, landslide, volcanic eruption, or meteorite. A tsunami can move hundreds of miles per hour in the open ocean and smash into land with waves as high as 100 feet or more.
From the area where the tsunami originates, waves travel outward in all directions. Once the wave approaches the shore, it builds in height. The topography of the coastline and the ocean floor will influence the size of the wave. There may be more than one wave and the succeeding one may be larger than the one before. That is why a small tsunami at one beach can be a giant wave a few miles away.
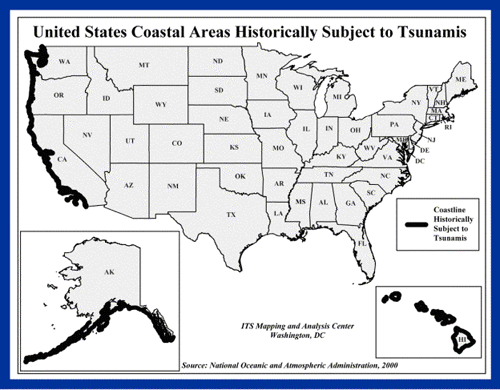
All tsunamis are potentially dangerous, even though they may not damage every coastline they strike. A tsunami can strike anywhere along most of the U.S. coastline. The most destructive tsunamis have occurred along the coasts of California, Oregon, Washington, Alaska, and Hawaii.
Earthquake-induced movement of the ocean floor most often generates tsunamis. If a major earthquake or landslide occurs close to shore, the first wave in a series could reach the beach in a few minutes, even before a warning is issued. Areas are at greater risk if they are less than 25 feet above sea level and within a mile of the shoreline. Drowning is the most common cause of death associated with a tsunami. Tsunami waves and the receding water are very destructive to structures in the run-up zone. Other hazards include flooding, contamination of drinking water, and fires from gas lines or ruptured tanks.
Know the Terms
Familiarize yourself with these terms to help identify a tsunami hazard:
Familiarize yourself with these terms to help identify a tsunami hazard:
Advisory
An earthquake has occurred in the Pacific basin, which might generate a tsunami.
An earthquake has occurred in the Pacific basin, which might generate a tsunami.
Watch
A tsunami was or may have been generated, but is at least two hours travel time to the area in Watch status.
A tsunami was or may have been generated, but is at least two hours travel time to the area in Watch status.
Warning
A tsunami was, or may have been generated, which could cause damage; therefore, people in the warned area are strongly advised to evacuate.
A tsunami was, or may have been generated, which could cause damage; therefore, people in the warned area are strongly advised to evacuate.
Take Protective Measures
During a Tsunami
The following are guidelines for what you should do if a tsunami is likely in your area:
- Turn on your radio to learn if there is a tsunami warning if an earthquake occurs and you are in a coastal area.
- Move inland to higher ground immediately and stay there.
| CAUTION - If there is noticeable recession in water away from the shoreline this is nature's tsunami warning and it should be heeded. You should move away immediately. |
After a Tsunami
The following are guidelines for the period following a tsunami:
- Stay away from flooded and damaged areas until officials say it is safe to return.
- Stay away from debris in the water; it may pose a safety hazard to boats and people.

Save Yourself - Not Your Possessions
Like everyone else in Maullin, Chile,, Ramon Atala survived the 1960 Chile earthquake. However, he lost his life trying to save something from the tsunami that followed.
Mt. Atala was Maullin’s most prosperous merchant. Outside of town, he owned a barn and a plantation of Monterey pine. In town, he owned a pier and at least one large building and also had private quarters in a waterfront warehouse.
Mt. Atala entered this warehouse between the first and second wave of the tsunami that struck Maullin. The warehouse was washed away and his body was never found.
It is unclear what he was trying to save. What is clear is that no possession is worth your life and that it is important to get to higher ground away from the coast and stay there until it is safe to return.
Download Plug-in
Some of the links on this page require a plug-in to view them. Links to the plug-ins are available below.
Last Modified: Wednesday, 11-Aug-2010 12:25:56 EDT via Fema
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)